If you’ve always dreamed of flying through the clouds, then learning how to become a pilot may be a top priority for you.

Whether you’re interested in flying for your own enjoyment or in pursuing commercial pilot training, aviation school could be the next step toward achieving your goals.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
The path to becoming a pilot can vary depending on what sort of flight certificate you’d like to pursue. You can check out the various options so that you can form a plan for your aviation success!
How to Become a Pilot
Becoming a pilot might seem like a big goal, but that doesn’t mean it’s out of reach. Breaking the process down into steps can help you see what’s involved in achieving this goal.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
Here’s how to go about the process of becoming a certified pilot:
- Pick your program. Aspiring pilots can choose from different types of schools, including flight schools and colleges with aviation programs. You can take a look at different options to see what’s best for you. It’s also beneficial to do an introductory flight at any school you’re considering to make sure that you enjoy the experience.
- Complete prep work. Before you can start pilot training, you’ll be required to pass a medical examination. You’ll also need to earn a student pilot license. The flight lessons can begin before you have the license, but you’ll need to obtain it fairly early in your training.
- Earn a private pilot license. To achieve this certification, you’ll take flying lessons, complete a written test, and pass a practical exam. With this license, you’ll be able to fly with passengers, but you won’t be able to charge for your services.
- Enhance your certifications. Once you’ve earned your private pilot certificate, you can add ratings to your credentials. Getting an instrument rating (IR) shows that you can use the plane’s electronic instruments to guide the plane at night or during inclement weather. A multi-engine rating qualifies you to operate larger aircraft with more than one engine.
- Become certified for commercial flights. To get paid for your flight services, you can earn a commercial pilot certificate. This requires more stringent requirements than a private license. You’ll be required to pass a more detailed medical exam, take tests, and accrue plenty of flight hours.
- Qualify to teach others. Additional credentials can allow you to teach flight skills to other pilot hopefuls. Giving flight lessons can be a strategic way to earn a living while working your way toward a career as an airline pilot. There are different levels of instructor ratings. The more you have, the more skills you’ll be able to teach.
- Get your airline transport pilot (ATP) certificate. After logging at least 1,500 qualifying flight hours, you can apply for your ATP license. This is the highest level of certification for airplane pilots. Anyone who wants to transport passengers for a living must have this type of license.
Depending on your goals, you could choose to stop after getting your private pilot license or to keep going until you have an ATP certificate.
Types of Pilot Certifications

There are different levels of certification for pilots, and each one allows you to take on different responsibilities. Understanding the differences can help you set a goal for which type of license you’d like to hold someday.
1. Student Pilot Certificate
While you’re learning to fly, you can apply for your student license. Once you have it, you’ll be able to take solo flights with your instructor’s supervision.
The requirements include passing a medical exam, taking a written test, and getting your flight instructor’s approval. You must be at least 16 years old.
2. Private Pilot Certificate

After logging 40 hours of flight time and taking a written test, an oral test, and a practical test, you may qualify for your private pilot license.
As a private pilot, you can fly yourself and a few passengers during the day. You can also start earning ratings and additional certificates.
3. Sport Pilot Certificate
With just 20 hours of flight time, you can apply for your sport pilot certificate. It authorizes you to fly two-seater aircraft.
You’ll be restricted to daytime flights and must stay under the clouds. This can be an ideal license option for people who are interested in flight as a casual hobby.
4. Commercial Pilot Certificate

To get paid for flight services—such as spraying crops or delivering cargo—a commercial pilot certificate is required.
Qualifying for this license requires hundreds of hours of flight time. It also requires a more stringent medical examination and additional written, oral, and practical tests.
5. Certified Flight Instructor Certificate (CPI)
If you want to teach others how to fly, you can pursue certification to become a certified instructor.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
Having your commercial pilot certificate is a requirement for getting approved as a flight instructor. As you teach others, you can earn flight hours that can count toward your next level of certification.
6. Airline Transport Pilot Certificate
The highest achievement you can get in pilot licensure is the airline transport pilot certificate. With it, you can receive payment to fly passengers from one place to another.
Accruing 1,500 hours of flight time is one of the main requirements for this certificate. Also, you have to be at least 23 years old.
Common Pilot Ratings

You can earn ratings to build on your basic license. Ratings allow you to fly in a greater variety of conditions, or they let you operate different types of aircraft. Here are some common pilot ratings:
- Instrument Rating. With a basic private pilot certificate, you can only fly at times when you can clearly see what you’re doing and where you’re going. Earning an instrument rating shows that you know how to use an airplane’s instruments to guide you. That way, you can fly at night, in the clouds, or in less-than-perfect weather.
- Multi-Engine Rating. To fly an airplane that has more than one engine, you can earn your multi-engine rating. Airplanes with multiple engines can fly higher and faster than single-engine planes.
- Seaplane Rating. Seaplanes use bodies of water for takeoff and landing. To operate this type of aircraft, it’s necessary to obtain a special rating.
- Helicopter Rating. To operate a helicopter, you can choose to earn a helicopter pilot license. If you already have a private pilot license, you can add a helicopter rating instead of starting from scratch with a new licensing program.
Each rating requires different qualifications, such as the number of training hours that you’ll need. There are also ratings that allow flight instructors to teach more advanced skills.
Aviation Careers & Salaries
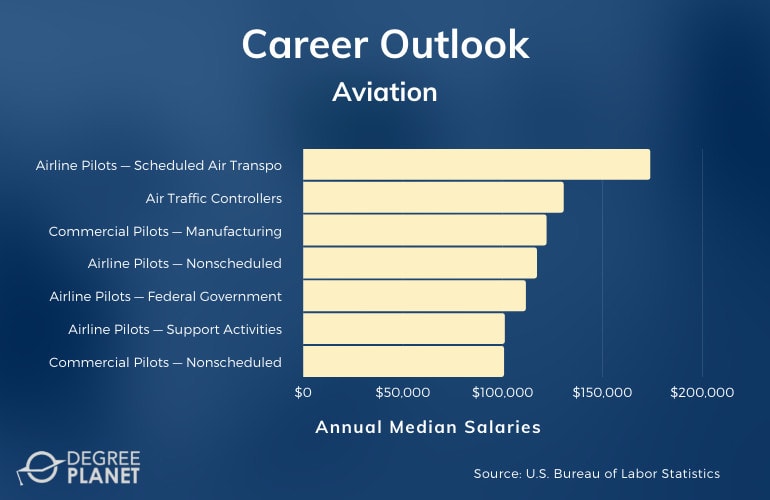
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary for pilots is $130,440.
| Careers | Annual Median Salaries |
| Airline Pilots — Scheduled Air Transportation | $173,780 |
| Air Traffic Controllers | $130,420 |
| Commercial Pilots — Manufacturing | $121,830 |
| Airline Pilots — Nonscheduled Air Transportation | $117,030 |
| Airline Pilots — Federal Government | $111,460 |
| Airline Pilots — Support Activities for Transportation | $100,910 |
| Commercial Pilots — Nonscheduled Air Transportation | $100,530 |
| Commercial Pilots — Support Activities for Air Transportation | $85,080 |
| Commercial Pilots — Ambulance Services | $83,210 |
| Commercial Pilots — Private Technical and Trade Schools | $81,980 |
In addition to these many piloting jobs, aviation students may also pursue careers as airport managers, transportation screeners, flight attendants, airplane mechanics, avionics technicians, and aerospace engineering technologists.
Choosing a Flight School

To make the most of your opportunity to go to flying school, it’s beneficial to make sure you choose a school that’s a good fit for you. You might want to think about characteristics like these to help you make the right choice:
- Aircraft selection. You can take a look at what airplanes a school has available for student use. You may want a training program that has a wide variety of aircraft or one that has the newest models.
- Cost. Some aviation schools have higher tuitions than others. Financial aid may make a dent in your costs, but it can still be helpful to keep price in mind as you compare schools.
- FAA approval. If getting approved as a pilot is your goal, then it’s critical to attend a school that is authorized by the Federal Aviation Administration to provide the certification that you want to receive.
- Location. You may want to choose a school that’s close to your home. If you’re willing to relocate, climate could play a role in your decision. At a school with year-round pleasant weather, you may have more opportunities to take to the skies.
- Track record. You can take a look at how long the school has been operating, how many students they’ve successfully graduated, and where those graduates have found employment after completing the program.
There’s no one school that’s best for every student, but there may be a program that’s the best fit for you.
Accreditation

For a respected college degree, it’s strategic to choose a regionally accredited school for your aviation studies. This type of accreditation is given to institutions that adhere to accepted standards for quality education.
If you change your educational plans and decide to switch to a different school, you’ll be more likely to receive credit for classes that were taken at a regionally accredited institution.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
In the same way, an accredited degree can be an admissions requirement for graduate programs. Employers value regional accreditation too, so it can be beneficial to have an accredited degree listed on your resume.
Financial Aid and Scholarships

Paying out of pocket for pilot training can be a challenge, but you might be able to finance some of your college studies with financial aid.
State and federal programs provide grants or low-interest loans for qualifying students. You can see if you’re eligible for government assistance by filling out the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA).
Private organizations sometimes provide tuition help as well. Your employer may even chip in, and your school might have scholarships available for some students. Various clubs and associations also offer need-based or merit-based scholarships.
Is It Hard to Become a Pilot?

Learning to fly takes time and dedication. To achieve your dream of flight, it helps to have the determination to stick with it as you earn one flight hour after another.
You’ll typically do a lot of studying to learn flight rules, airplane parts, and aircraft operation. For a college aviation degree, you may take classes that cover topics like aviation meteorology, air traffic control, and airplane flight instruction.
Pilots also have to be in suitable physical condition. It’s necessary to get medical clearance, and some health conditions can prohibit you from becoming a pilot.
What Qualifications Do You Need to Become a Pilot?
Here are several key components to getting your flying license:
- Medical exam. An FAA approved doctor will need to sign off on your suitability for flight.
- Student license. Before you can take a solo flight, a student pilot certificate from the FAA is required.
- Written test. Your ground instruction will prepare you for the written exam.
- Practical test. You’ll also take an oral test and demonstrate your flying skills.
These steps are essential for earning a private pilot certificate.
How Much Does It Cost to Become a Pilot?

To become a pilot, you’ll pay instructor fees for each stage of your training, and you may need to factor in airplane rental costs as well. Instructors and rentals are usually paid by the hour.
The low end for a private pilot license may be around $11,000. At the high end, you may pay around $36,000 to wrap up your commercial training and get a multi-engine rating. If you earn a bachelor’s in aviation, you may pay between $300 and $800 per credit hour in addition to flight fees. Most bachelor programs consist of 120 credit hours.
Do You Need a Degree to Be a Pilot?
While you don’t necessarily need a degree to become a pilot, it can certainly help your career prospects.
There are some aviation jobs that don’t require a degree. For example, you may not need a college education to give aerial tours, spray crops, or provide corporate transportation.

Many airlines prefer degrees, though. That’s especially true of the major airlines. If you want to be competitive for those jobs, it’s necessary to have a bachelor’s degree. Without a degree, you’re more likely to qualify for work with a regional airline than a major one.
How Much Do Pilots Make?
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, pilots earn a median annual salary of $130,440. Airline pilots tend to earn more than commercial pilots. For airline pilots, the annual median is $160,970. Most make between $80,920 and $208,000 each year. Those who work in scheduled air transportation earn a median annual salary of $173,780.
The median salary for commercial pilots is $93,300, and most earn between $47,570 and $200,920. Nonscheduled air transportation offers the highest employment for commercial pilots, and the median pay for this sector is $100,530 per year.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
Working as an air traffic controller is a related option. That role pays a median of $130,420 per year (Bureau of Labor Statistics).
How Long Does It Take to Become a Pilot?

It’s possible to earn a private pilot certificate in just a few months. Being ready to fly professionally can take much longer, though.
For many aspiring pilots, it takes around 5 years to qualify for an ATP certificate. That allows students plenty of time to accumulate the required 1,500 hours of flight time. A bachelor’s degree is a strategic way to prepare for a career as an airline pilot. It usually takes 4 years of full-time study to graduate with a bachelor’s.
During your studies, you can earn several certificates and ratings. You may even have your ATP certificate by the time you finish your program.
What’s the Difference Between a Part 61 vs. 141 Pilot Certificate?
You can earn your pilot license with Part 61 training or with Part 141 training. Here’s how the two options differ.
| Part 61 | Part 141 |
|
|
Part 61 is often more suitable for hobbyists, and Part 141 is common for those who have a professional flying career in mind.
Getting Your Pilot Degree Online

If you want to pursue an exciting career as a pilot, getting a bachelor’s degree can help equip you with advanced training and qualifications.
During a college flight program, you could also have opportunities to earn certificates and ratings. Plus, a degree is often required for employment with major airlines. There are even accredited colleges that offer online aviation degree programs.
If you pair online coursework with local flight training, you might be able to complete your college degree in a quick, flexible format. You may want to take a look at accredited online schools to learn more about your options.

