The best schools for music production teach studio skills that can enable you to create your own recorded music. The study of music production blends both artistic and technical interests.
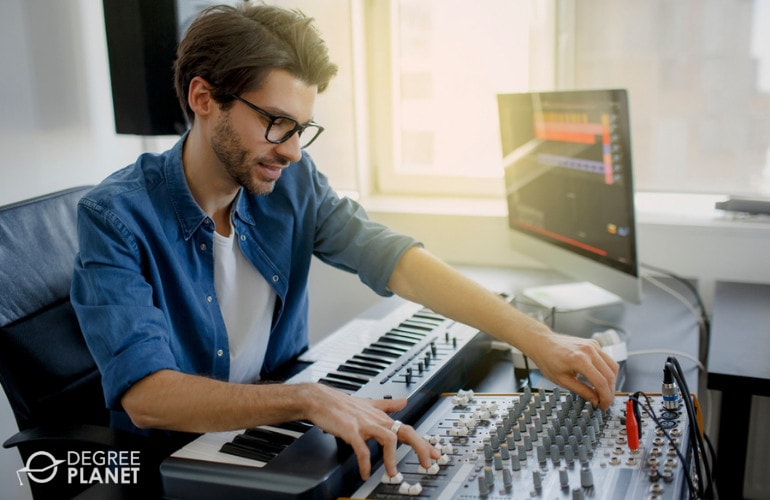

Knowledge of music production can be useful for musicians in educational and recreational settings. It’s also strategic for those who wish to pursue careers in the commercial music industry.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
Read on to learn more about college majors and career prospects in music production.
Best Schools for Music Production

Majoring in music production is becoming more popular, and degrees in music production can take many forms.
A Bachelor of Arts in Music Production provides a strong foundation in core subjects and the humanities, while a Bachelor of Science emphasizes how the technology works. On the other hand, a Bachelor of Fine Arts will focus more on the artistic and performance aspects of music.
Topics studied in music production schools often include:
- Music theory
- History of recording and the commercial music industry
- Aural skills
- Keyboard skills
- Different genres of music
- Basic knowledge of recording equipment
- Hardware and software for recording and editing music
It is beneficial to screen and evaluate music production colleges to determine their credibility and to see which ones best align with your goals. Some schools may do a better job than others at providing the knowledge and experience you’re looking for.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
A number of audio production schools offer degree programs both on campus and online. On-campus programs usually have studio labs where you can gain hands-on experience working with recording technology and equipment.
You may also be able to earn your degree in a hybrid format, having a combination of online and on-campus commitments. For some online music engineering schools, you may be expected to own your own recording equipment.
Music Production Careers & Salaries
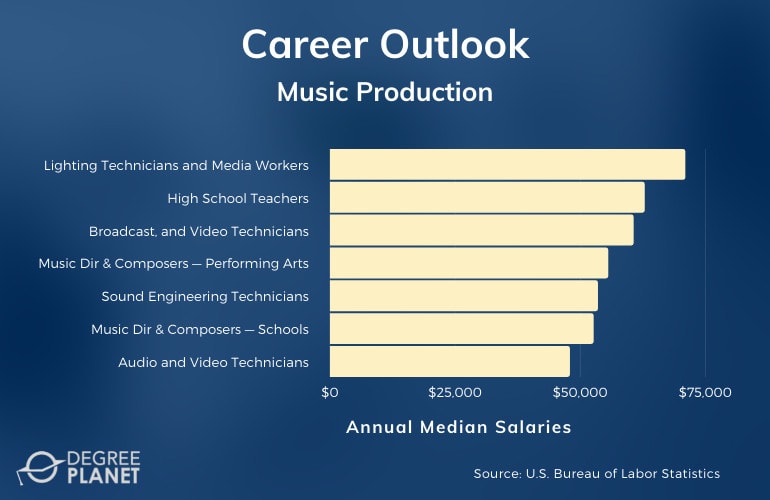
Music production training can be utilized in the commercial recording industry, but it can be applied to other settings as well.
For instance, churches and schools often need professionals who are knowledgeable about audio technology for services, recordings, events, or performances. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, here are some careers related to music production, along with their median annual salaries.
| Careers | Annual Median Salaries |
| Lighting Technicians and Media and Communication Equipment Workers | $73,460 |
| Music Directors and Composers — Elementary and Secondary Schools |
$61,950 |
| High School Teachers | $61,820 |
| Broadcast, Sound, and Video Technicians — Motion Picture and Sound Recording Industries | $60,540 |
| Sound Engineering Technicians | $60,500 |
| Music Directors and Composers — Performing Arts Companies | $50,150 |
| Audio and Video Technicians | $48,820 |
| Music Directors and Composers — Religious, Grantmaking, Civic, Professional, and Similar Organizations | $48,420 |
| Broadcast Technicians |
$44,740 |
| Broadcast, Sound, and Video Technicians — Radio and Television Broadcasting | $37,750 |
Music production knowledge can be useful in media and entertainment industries as well as in educational settings. Music directors and composers are usually employed by performing arts companies, elementary and secondary schools, or religious, grantmaking, civic, professional, and similar organizations. Many professionals are also self-employed.
Music Production Bachelor’s Curriculum & Courses

Here are examples of courses you might take while earning a bachelor’s degree in music production:
- Principles of Audio Technology: In this course, you’ll learn the basics of using various types of audio equipment.
- Critical Listening Lab: This course focuses on developing your skills in recognizing and paying attention to the details of how a piece of music sounds.
- Production Analysis Lab: In this course, you’ll learn to evaluate the emotional effectiveness of a recording.
- Audio and MIDI Systems for Music Production: In this course, you’ll learn about the Musical Instrument Digital Interface and how to connect computers, microphones, instruments, and other devices together for a recording session.
- Hybrid Production: In this course, you’ll learn how to use analog technology in conjunction with digital technology in the music studio.
- Creative Production Skills: In this course, you’ll study the artistic and soft skills needed to work as a music producer, such as collaborating with artists and clients to define the goals of a recording project and choosing vocalists and instrumentalists.
- Music Production for Records: In this course, you’ll learn about the process of creating a complete commercial record, such as choosing which songs to include and what order they should be in.
- Advanced Recording Techniques: In this course, you’ll learn complex ensemble microphone techniques and other advanced skills.
- The Business of Music Production: In this course, you’ll learn about legal and financial aspects of the music industry—including copyright, deal structures, client relationships, project planning, product distributions, and the collection and distribution of royalties.
- Advanced Production Projects: In this course, you’ll create your own recordings to demonstrate your knowledge and skills.
Exact course titles and requirements will vary at different schools.
How to Choose an Online School for Music Producing

Here are some factors to consider when choosing an online school for music producing:
- Job placement rate. What have previous students done after graduation? How many have gone on to establish careers in music production or related fields? Has the school produced any notable alumni?
- Collaboration. Does the school offer opportunities to interact with classmates and instructors? Because the creation of music is often a team effort, you may want your student experience to include opportunities to work with other musicians and receive feedback from instructors. Even if a degree program is entirely online, it may still provide these opportunities via online platforms.
- Musical genre. Does the program focus on your preferred genre of music? You may want to find a program where the instructors and other students share similar musical interests.
You may want to research a lot of different schools and programs before choosing where to apply.
Music Production Major Admissions Requirements

Here are some common admissions requirements for bachelor’s degree programs in music production:
- High school diploma or GED
- Official high school transcripts
- Essays or personal statements
- Auditions or demo recordings
Some schools may also require SAT or ACT scores, but a growing number of schools are no longer requiring them. At some colleges and universities, applicants must first be accepted into the school as a whole. They then fill out a second application or go through an audition process to specifically become a music production major.
Colleges for Music Production Accreditation

Before applying to any given college or university, you may want to find out if the school in question has regional accreditation.
Regionally accredited schools are regularly evaluated by their accrediting agencies to ensure that they meet certain basic standards in terms of their curricula, instruction, facilities, and more. Attending a regionally accredited school can be a qualifier for some forms of financial aid, and it can impact the transferability of your earned credits.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
You can usually find out about a school’s accreditation status by checking their website. You can also learn more about regional accreditation in general by visiting the Council for Higher Education Accreditation (CHEA).
Financial Aid and Scholarships

As you plan to get your college degree, you might be concerned about how you will pay for it. There are many forms of financial aid available for prospective students who qualify, including online students.
You might qualify for state or federal financial aid, and schools often have grants or scholarships that they award to select students based on need or merit. Some employers also have programs to help their workers fund their education.
For many students, the first step to obtaining financial aid is to fill out the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA).
What Is Music Production?
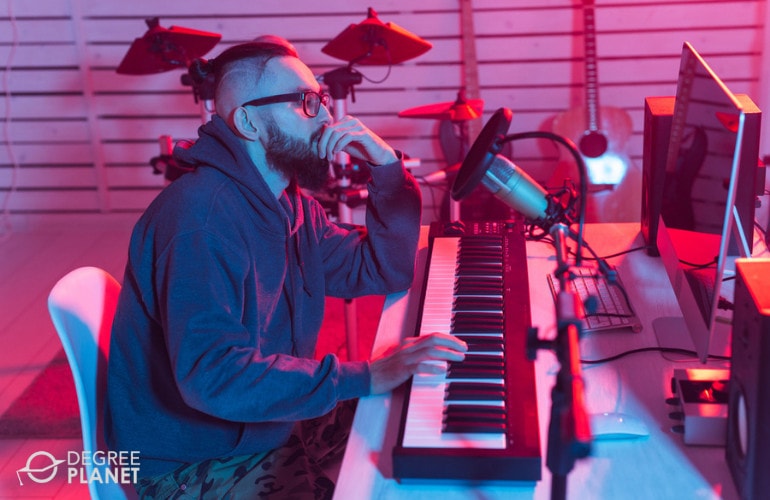

Music production is the study of how to record music. The field includes the study of music itself as well as how to make use of computers and other technology to capture performances.
As a music production major, you could learn about different devices, such as different types of microphones and their sound qualities. You can also learn how to analyze artistic aspects of music, record music, and refine recordings through the editing process. Music production usually takes place in studios, but it could potentially be practiced anywhere with a phone or laptop.
Is Music Production a Good Major?
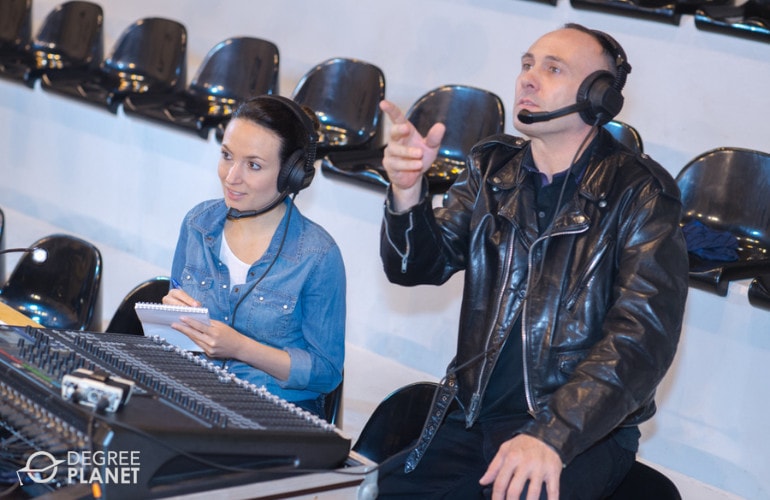

Yes, music production is a good career for many undergraduate students. Music production provides a creative outlet as well as opportunities to become skillful with a variety of different types of technology.
Career paths related to the field of music production include music directors and composers, musicians and singers, and sound engineering technicians. Employment of sound engineering technicians is currently projected to grow by 17% percent over the next decade, which is much faster than average (Bureau of Labor Statistics).
The music production field is competitive, and a music production major can be advantageous for students who are very passionate about the subject.
What Can You Do with a Music Production Degree?
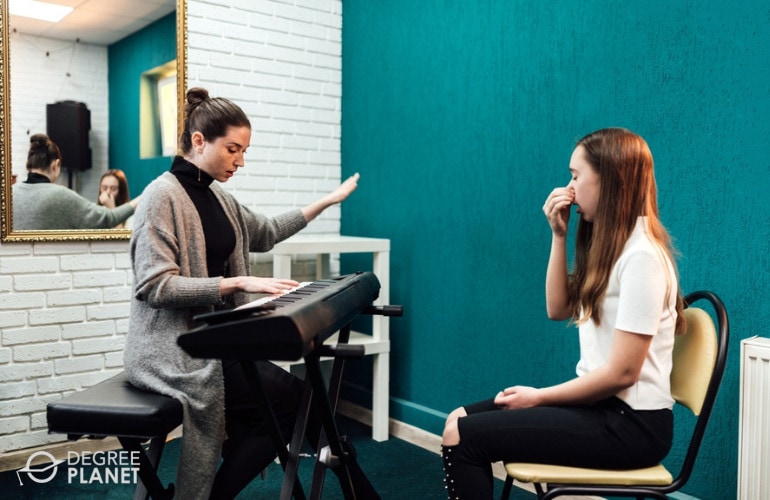

While many music production graduates want to become commercial record producers or musicians, there are other opportunities in this field.
For instance, knowledge gained from a music production program could be useful for an audio technician who works at a studio or an event venue. Sound engineering is another common career path. Some professionals become music directors or instructors for schools, churches, or music conservatories.
Graduates who are interested in teaching music in a K-12 public school setting usually earn their music teacher certification, which can vary by state.
Earning an undergrad degree in music may provide a path to pursue even more specific interests. If you are interested in both music and cultures, for example, a growing number of schools offer an on-campus or online masters in ethnomusicology that may be worth looking into.
How Much Do Music Producers Make?
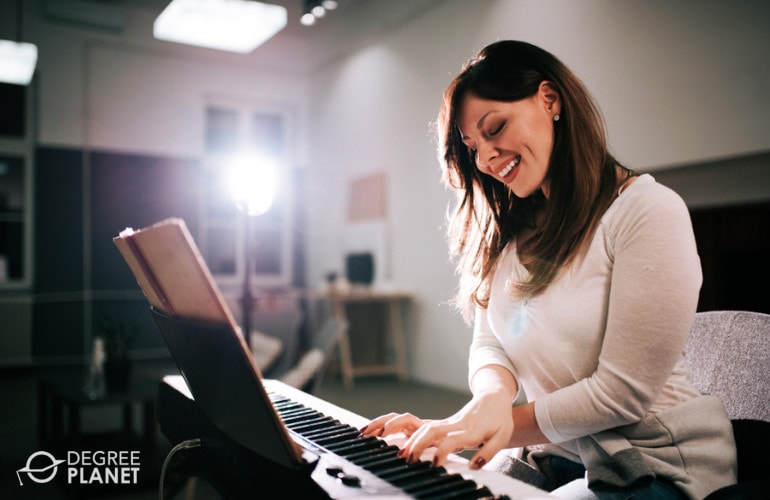

The Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that music directors and composers earn a median annual salary of $49,130, with most earning between $24,440 and $123,800.
The median salary for sound engineering technicians is $60,500, and the median for audio and video technicians is $48,820 (Bureau of Labor Statistics). Many music producers, musicians, and recording artists work on a freelance basis, so their earnings are subject to frequent fluctuations.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
The specific salary that a person can earn in music and audio production careers can vary widely, depending on a number of factors. Common determining factors include work experience, chosen industry, employer, and geographic location.
What Do Music Producers Do?
Music producers oversee the process of recording music. In addition to being technologically and musically literate, they also need to be familiar with the business side of music. They are often responsible for ensuring that recordings are completed on time and within budget.
Music producers may have musicians perform a piece of music multiple times and then choose which takes will go on the final album. They can also make other types of artistic decisions, such as deciding which instrument should play a certain line of music or how much the volume should fluctuate at different intervals.
How Long Is Music Production School?

A bachelors degree program in music production or any other field can usually be completed in 4 years if you follow a traditional 16 week semester schedule and enroll as a full-time student.
Some music degrees online provide more flexibility. For instance, programs with accelerated 8 week classes could enable you to finish your degree sooner if you study full-time and take classes year-round. If you take classes part-time, you may need more time to finish your degree.
What’s the Difference Between a Music Producer vs. Engineer?
Some people use these terms interchangeably, but they are technically different roles. Here are some of the key differences between a music producer and an audio engineer:
- Music producer: The producer oversees the recording process and makes artistic decisions about what a track should sound like. Producers have more managerial responsibility in the studio than engineers.
- Music engineer: During a recording session, the engineer oversees the equipment and its use, running the sound board to ensure that ideal sound is achieved. Many music producers actually start their careers as audio engineers.
There is some overlap between these two roles. For example, both producers and engineers need to have a good ear for music and need to know how to utilize the available technology in the studio. In some cases, one individual may perform the tasks of both the producer and the engineer.
Is Music Production School Worth It?

Yes, music production school is worth it for many students. A music production program can help you develop skills that are useful in the fields of music and music education. In this type of program, you can become familiar with all kinds of audio technology.
You can learn how to analyze music, and you could also learn how to help artists and performers find ways to improve their craft. Many positions related to music production are experiencing positive job growth, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. For instance, music directors and composers are expected to see 6% job growth over the next ten years.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
Meanwhile, jobs for sound engineering technicians are expected to grow by 17% over the same time period, and employment for audio and video technicians is projected to grow 26% (Bureau of Labor Statistics).
Best Universities Offering Bachelors in Music Production Degree Programs
Methodology: The following school list is in alphabetical order. To be included, a college or university must be regionally accredited and offer degree programs online or in a hybrid format.

The Academy of Art University offers a Bachelor of Fine Arts in Music Production. Classes are 7.5 or 15 weeks long and offered both online and in-person. To graduate, students must complete 132 credit hours with a GPA of 2.0 or higher. Applicants may apply online with copies of their official transcripts.
Academy of Art University is accredited by the WASC Senior College and University Commission.

Berklee College of Music offers a Bachelor of Arts in Music Production. Students must complete 120 credit hours to graduate. Those interested in the program must submit an online application along with copies of their official transcripts, two letters of recommendation, and either a written admissions essay or a video essay.
Berklee College of Music is accredited by the New England Commission of Higher Education.

Bethel University offers a Bachelor of Music in Music Production. Students must complete 124 credit hours to graduate. Applicants must have a GPA of 2.25 or higher and submit an online application along with copies of their official high school transcripts and ACT or SAT test scores.
Bethel University is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission.

Hampton University offers a Bachelor of Science in Music with an emphasis in Audio Production. Students must complete 120 credit hours and an internship to graduate. Those interested in the program may apply online through the school’s website. Applicants with a GPA of 3.3 or higher don’t need to submit SAT or ACT scores.
Hampton University is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges.

Millersville University offers a Bachelor of Science in Music Production with a concentration in the Music Industry. To be eligible for the program, applicants must submit applications to both the Millersville Admissions Office and to the Department of Music. An audition must also be completed.
Millersville University is accredited by the Middle States Commission on Higher Education.

New York University offers a Bachelor of Music in Music Technology. To graduate, students must complete 128 credit hours. Those interested in the program must submit an artistic portfolio with three samples, a current resume, a self-reported academic record, and ACT or SAT scores.
New York University is accredited by the Middle States Commission on Higher Education.

Northwest University offers a Bachelor of Arts in Audio Production. Students must complete 125 semester credit hours to graduate. To be eligible for the program, applicants must submit copies of their official high school transcripts and SAT or ACT test scores.
Northwest University is accredited by the Northwest Commission on Colleges and Universities.

Rowan University offers a Bachelor of Science in Music Industry. Students must complete 120 credit hours to graduate. To be eligible for the program, applicants must have a minimum GPA of 2.7 and submit an admissions essay, a portfolio, and a recommendation from a teacher.
Rowan University is accredited by the Middle States Commission on Higher Education.

The University of Southern California offers a Bachelor of Music in Music Production. The program can typically be completed in 4 years. To graduate, students must complete 132 credit hours and a final capstone project. Applicants must submit a portfolio along with their application. An in-person performance audition and a theory exam are also required.
The University of Southern California is accredited by the Western Association of Schools and Colleges.

Western Michigan University offers a Bachelor’s in Multimedia Arts Technology with an emphasis in Music. Students in the upper-level courses are given the opportunity to intern at the school’s recording studio. Applicants must submit their high school transcripts and ACT or SAT test scores.
Western Michigan University is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission.
Getting Your Music Production Degree Online

If you have decided that earning a music production degree is right for you, there are many possible program options for you to choose from.
An online degree program, such as an online music production or an online music technology degree, could provide you with the convenience of learning from home or anywhere with an Internet connection. There are online learning platforms available that allow you to easily communicate with classmates and instructors and receive feedback to hone your craft. Studying music production can help you develop both your creativity and your technological proficiency.
If you’re ready to begin your educational journey, why not start exploring accredited colleges and universities today?

